Table of contents
Cloud computing, cloud data – these expressions have gained popularity in the last years. Millions of companies use the cloud and significantly benefit from its key features – financially, but also in terms of efficiency, the comfort of file storage, or team collaboration.
We’re going to show you what cloud computing is, what kinds of clouds are there and how you can benefit from a business cloud alltogether.
Cloud computing – what is it?
Cloud computing (also referred to as an internet cloud) is a network of connected servers. Within this network, you can use services such as:
- Disk space (Google Disk, OneDrive, Dropbox),
- Mailbox (Gmail, Outlook),
- Internet communicators and video conference tools (Google Meet, Skype, Zoom),
- Cloud applications, like a text editor or online calculation sheets (Google Docs, Excel in OneDrive),
- Set of services for developers dedicated to creating web or mobile applications and other IT products (Google Cloud Platform, Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure).
You don’t have to install any software on your device to use the cloud – you have constant access to files and applications via an internet browser. Provider’s devices are constantly on and connected to the internet 24/7. For these devices to operate without obstacles, the focus in data centres should be on suitable temperature and humidity. The devices should also be secured against damage, water or fire and their access should be strictly monitored.
Technological giants, businesses such as Google, have many connected server rooms (called data centres). Thanks to that Google Cloud products are available globally, and services run just as fast in Warsaw as in New York or Sydney.
The Google Cloud Network – map presenting the fibre connections between Data Centers
Private, public, hybrid, multi-cloud – types of clouds
Companies can use various types of computing clouds:
- private cloud – includes exclusive sharing of cloud space within the internal network; the environment is isolated, and the company does not share the cloud with other users;
- public cloud – devices belong to external service providers (e.g., Google or Microsoft) and are part of the global network; a public cloud offers many ready services, for example an application for communication or infrastructure services;
- hybrid cloud – a combination of a public and private cloud or public cloud with on-premise data centre.
Cloud for businesses – use cases
Cloud computing should not be associated only with disk space integration. In most cases, it’s a set of advanced out-of-the-box tools and services. Here are some examples of how companies can use a cloud:
- storing files in a cloud, instead of on employees’ computers or external drives,
- team edition in real-time – changes made in one online file will be saved automatically and instantly available to co-workers,
- automatic back-up and retrieving files,
- setting up a website in a cloud, which guarantees better stability and cost transparency than any hosting,
- creating an application using cloud services.
Here you can check examples of cloud usage in companies:
- How does CCIG Group ensure data security with Google Workspace?
- What’s it like to collaborate with people across 5 different continents
- How Wizerunek w Sieci improved the management of over 30 websites
Advantages of using cloud computing
- Better collaboration – team edition of documents within the cloud environment enables cooperation in real-time and cancels the necessity to send corrected versions of files repeatedly,
- Access from an internet browser – platforms, such as the Google Workspace, can be accessed from any device: a computer with Windows, Linux, macOS or a smartphone;
- Safety – data stored in a cloud is encrypted and password protected; if a computer gets damaged or stolen, the data will remain safe;
- Access control – an administrator can manage authorization levels and control who has access to which files,
- Disk space and computing power – cloud resources are almost unlimited, thanks to what you can use as much as you need,
- Services that accelerate development – you can leverage cloud services to create new or boost existing applications.
Flaws of cloud computing
- Dependency on service provider – a cloud is a model in which you purchase access to resources physically belonging to a provider. In a case of infrastructure malfunction, accessing your data will be difficult or even impossible,
- Security – is an area that generates a lot of discussions. The popular service providers (e.g., GCP, AWS) fulfil many safety requirements and perform regular audits; however, the data stored in a cloud remain within the service provider’s solution and, thus, it’s hard to introduce individual security mechanisms,
- Complex calculation model – cloud services are billed in a different way than hosting services or own data centre maintenance, which may cause some difficulties,
- Overpayment for services due to false configuration – you should pay close attention to configuring cloud services because an overlook may cost you much; if you don’t have any experience with a cloud, you can rely on a Google Cloud partner,
- The necessity to introduce changes in a workflow – implementing cloud solutions should be combined with a partial change in a work course, increasing employees’ conscience in terms of a cloud, or sometimes obtaining new competencies (e.g., DevOps), which is associated with extra finances.
How much does an enterprise cloud cost?
Cloud services are scalable and can be adjusted to business requirements. A smaller team with a few employees has access to similar services as an international corporation with thousands of employees. Adequately, a new startup can build its own cloud infrastructure by selecting those services used by technological giants. In both cases, companies will be billed depending on the plan, a number of licences or computing power usage level.
Billing models differ between kinds of cloud services. The cost of business packages for cooperation is charged other than the cost of infrastructure services for application development.
Payment model for business applications (on the example of Google Workspace)
A cloud business app suite, in many cases, consists of a mailbox with its own domain, disk space, online text editors, sheets, a chat or a tool for video conferencing. Popular examples of such corporate solutions are Google Workspace or Microsoft 365 and other services like SharePoint Online.
Providers come forward with solutions in packages that vary in terms of the available functions and license prices. Prices are usually presented in the following form: type of package / one account / on a monthly basis.
Below is a table comparing the Google Workspace Business packages (formerly Google Workspace) with price per license indication.
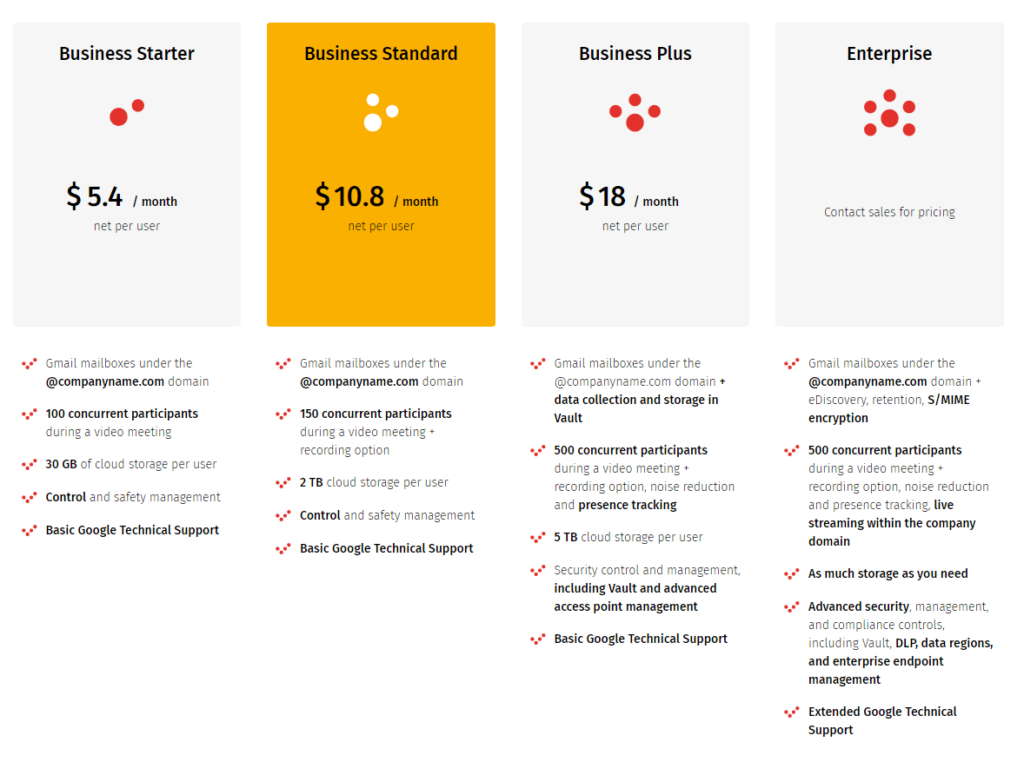
Therefore, for example:
- an entrepreneur runs a one-person business; he purchases one Business Starter licence on Google Workspace and pays $5.2 per month;
- a 10 employees team wants to give access to Google Workspace in the Business Standard package to all of them; its monthly payment is in total $108,
- another 100-employees team needs Business Standard accounts for its 80 employees and higher licences of Business Plus for 20 employees; its monthly payment is $1224 ($864 for the Standard accounts and $360 for the Plus accounts).
Here you’ll find more information about Google Workspace pricelist.
Payment model for cloud infrastructure services (on the example of Google Cloud Platform)
Payment for the cloud infrastructure services is calculated concerning the configuration method and usage level. Costs are billed on a minute, sometimes on a second basis.
For instance, the cost of one of the most popular Google Cloud Platform services – Compute Engine, a virtual machine service – will depend on :
- type of the machine – its RAM memory, vCPU or disk space,
- localization of the data centre – the service price will be different for a server located in, i.a., Las Vegas, London or Tokyo,
- data transfer and network usage – depending on whether you are using public internet or the Google Cloud network,
- load – if the application uses little computing output, the service’s cost is low; if traffic intensifies, the service scales up together with the cost.
Google Cloud Platform consists of nearly 200 services. Each of them has a different price depending on several factors. The cost of infrastructure within the Google Cloud can only be defined with technical knowledge of the application. To calculate the exact cost, you can use dedicated calculator.
It’s good to use the cloud with the support of a certified Partner who knows the solution and can indicate possibilities for cost optimization.
Google Cloud – an enterprise cloud popular among companies
Google Cloud is a public cloud created and developed by, of course, Google. It comprises two leading solutions: Google Workspace (formerly G Suite) and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Google Workspace for better collaboration and files management
Google Workspace (formerly G Suite) is a set of cloud tools for productivity and communication.
Google Workspace consists of the following tools:
- Gmail – mailbox in your own domain,
- Calendar – an online calendar that allows to plan meetings and joint activities easily,
- Google Chat – an online communicator,
- Google Meet – a video conference tool, continuously extended with new functionalities (i.a., joint drawing on the remote Jamboard or surveying),
- Google Drive – cloud disk,
- Google Docs – file editor where many people can carry out the edition at once,
- Google Sheets – online calculation sheets,
- Google Slides – an application that allows to create and edit multimedia presentations,
- Google Forms – a tool for creating surveys and managing the analysis results,
- Google Keep – application for creating and joint editing of notes,
- Google Sites – website editor,
- Google Admin – administrative console.
Google Workspace allows efficient cooperation and document control. The changes introduced by one person are instantly visible by other colleagues, and Google saves the whole editing history. You do not need to constantly press Ctrl+S nor forward the corrected file version for the fifth time. All documents are located on the Google Disk and the files’ safety is controlled by an administrator from the comprehensive administrative console.
Here you will learn more about Google Workspace.
Google Cloud Platform for apps development
The Google Cloud Platform (abbreviated to GCP) is a package of computing services for software programmers and system administrators. These technologies are similar to those used by Google to develop its tools and applications.
Google Cloud Platform components can be selected individually to create your own adjusted infrastructure. The services include, among others:
- scalable virtual machines with almost unlimited computing power (the Compute Engine service),
- a platform for managing Kubernetes technology clusters (Google Kubernetes Engine),
- tools for quick deployments and changes, also for applications in containers (App Engine, Cloud Functions, Cloud Run services),
- cloud databases (Cloud SQL, Datastore),
- data warehouses and BigData analysis services (BigQuery),
- out-of-the-box machine learning and artificial intelligence models,
- a platform for running Internet of Things projects.
Using the Google Cloud Platform services, you can host a simple website, maintain an extensive application or develop an advanced system using ML/AI models.
All Google Cloud Platform customers have access to the same services – global corporations, SMB companies, or new professional startups. The usage scale depends on the each specific spectrum of needs. Companies of all sizes can use the same cloud implements as PayPal, eBay, or Twitter, and pay proportionally less, depending on the actual usage.
